What Is A Periodontist?
A periodontist is a dentist who has had further extensive training to specialise in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of periodontal disease. Periodontists are also trained in the placement and maintenance of dental implants, management of oral inflammation, cosmetic 'gum' procedures, and other 'gum and bone related' treatment.
Periodontal disease is common and periodontists often treat more problematic periodontal cases, such as those with severe 'gum' disease, a complex medical history, or patients with dental anxiety. Periodontists focus on management of the gums, bone and other supporting structures of teeth and implants.
A periodontist works with your dentist and hygienist as part of a dental team to manage your periodontal or implant concerns.


What Is Periodontitis?
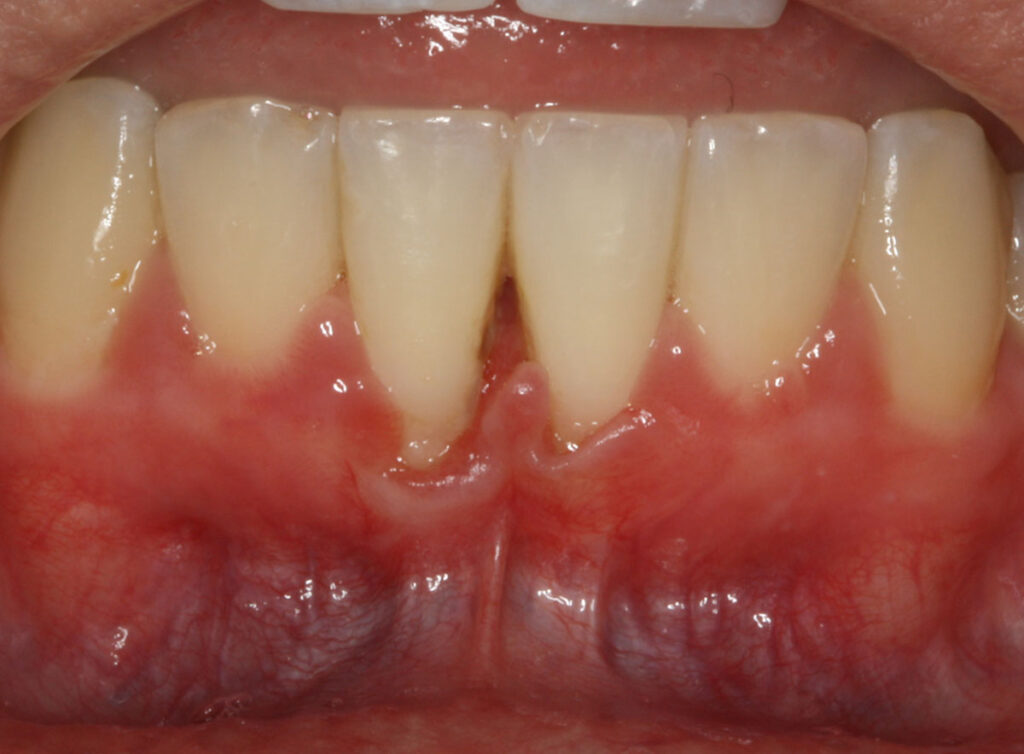
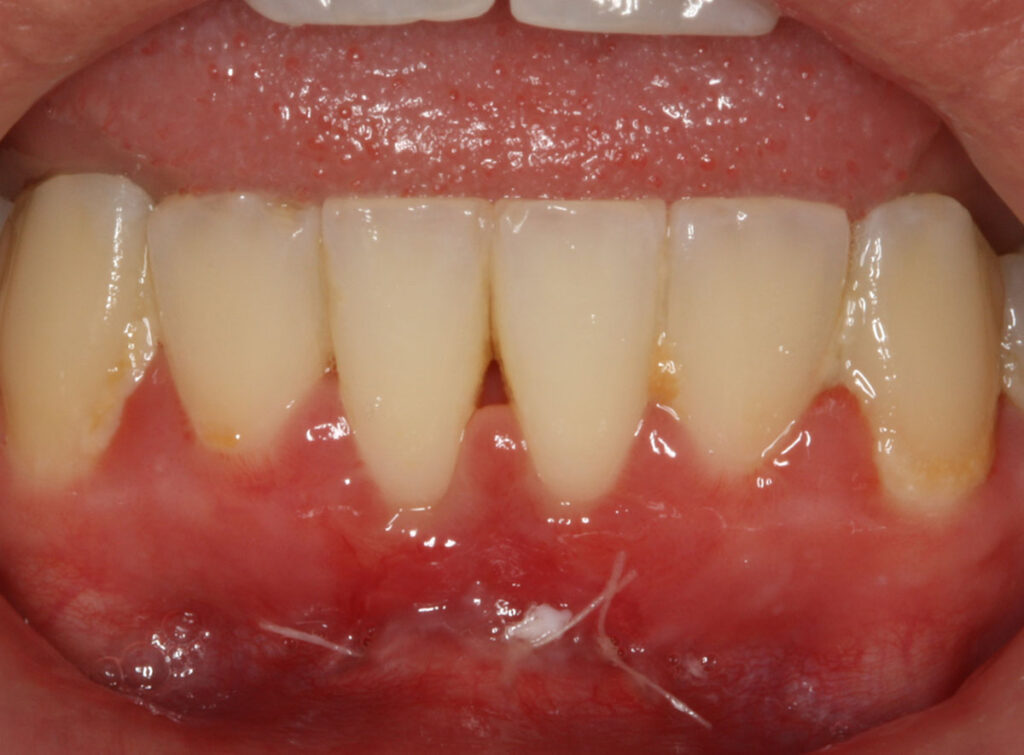
Periodontitis is a disease of the gums and bone that is caused by plaque bacteria on the teeth. The inflammation and infection caused by the build-up can lead to irreversible damage to the supporting structures, leading to shrinkage of the gums and bone. The gums become red, swollen, and tend to bleed easily. They separate from the teeth, forming pockets (spaces between the teeth and gums) and become infected. Ongoing damage to the supporting structures may lead to teeth becoming loose, gum abscesses arising, and eventual tooth loss. Several factors can render periodontitis to be more prevalent or severe, including smoking, diabetes mellitus, and immunosuppression.
Periodontitis can be managed through different procedures. A periodontist will assess the gums and supporting structures and be able to recommend various treatment options to best treat any gum or bone related disease.
Procedures
Debridement involves cleaning the teeth to remove plaque and calculus from the root surface above and below the gum line. This is the most common treatment for periodontitis and is considered to be 'deep cleaning', usually to areas deeper under the gum line than regular cleaning. This does not involve 'cutting' of the gums and can stabilise the periodontal disease in the majority of patients.
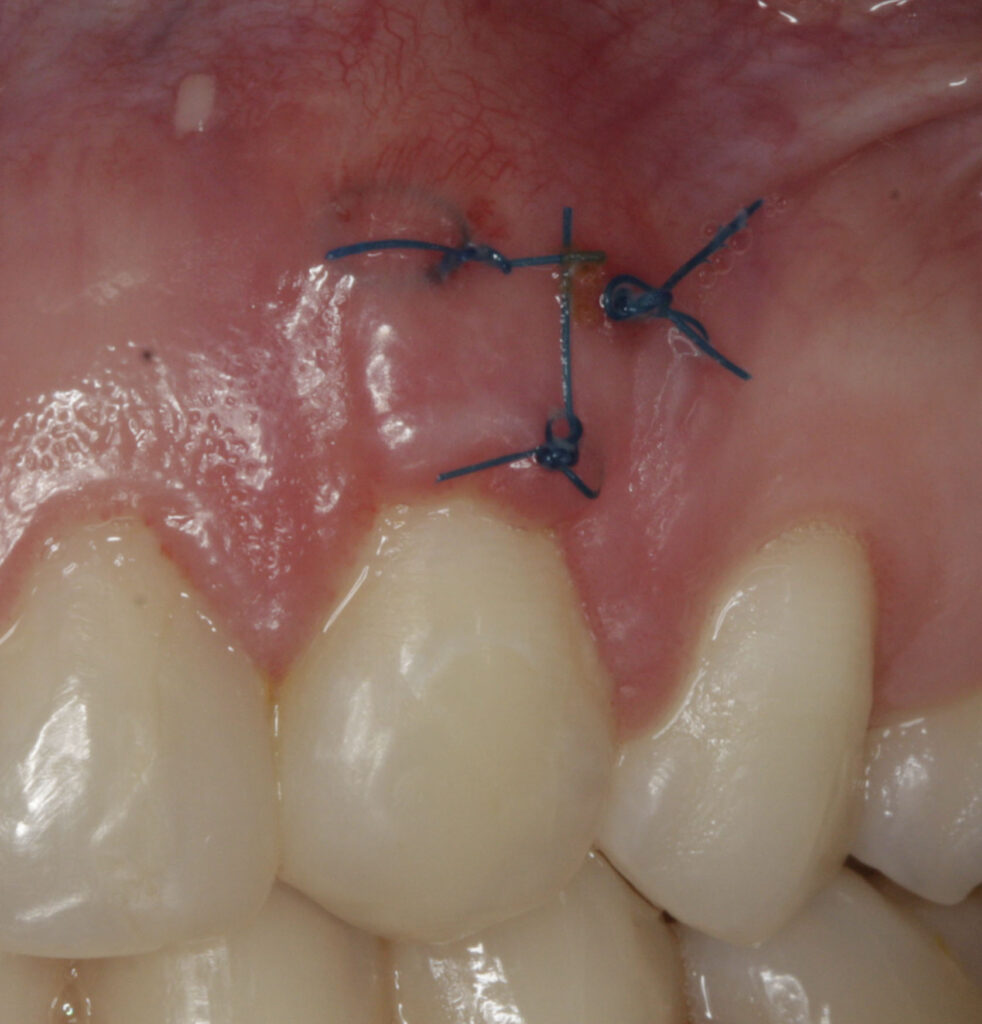
Periodontal surgery involves reshaping or lifting of the gums to improve access and visibility to hard-to-reach areas around the teeth. This allows removal of plaque and calculus from inaccessible, below the gum margin areas.
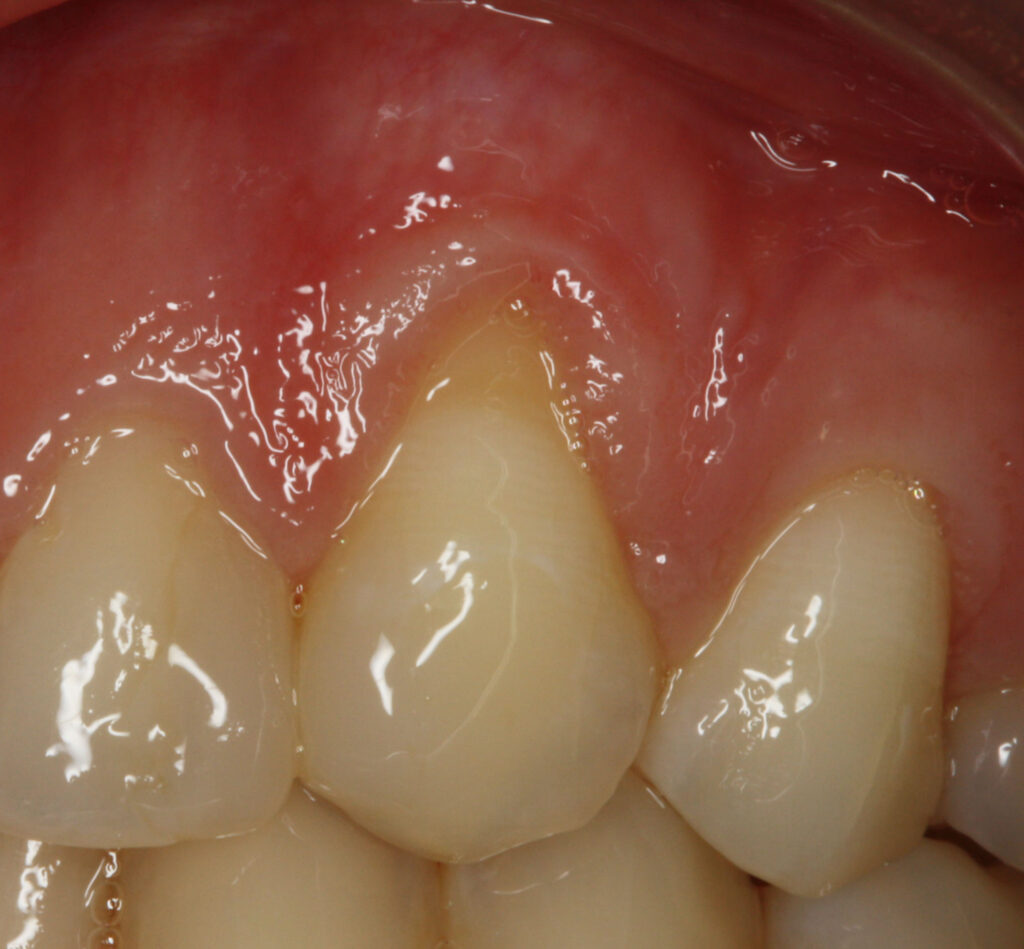
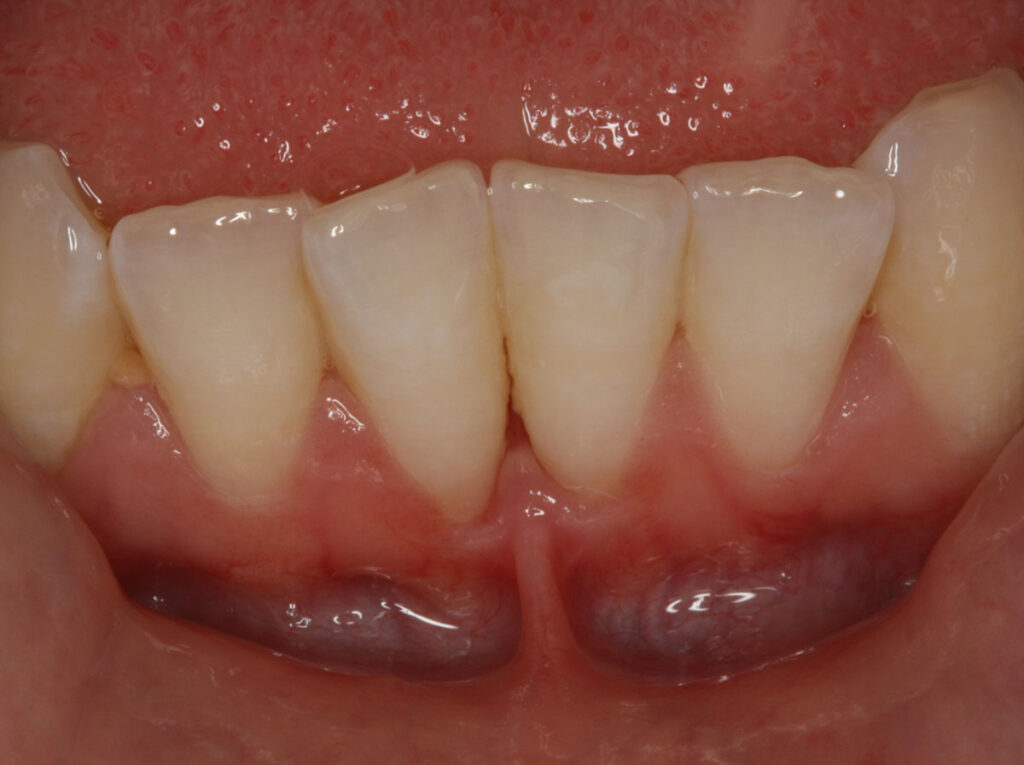
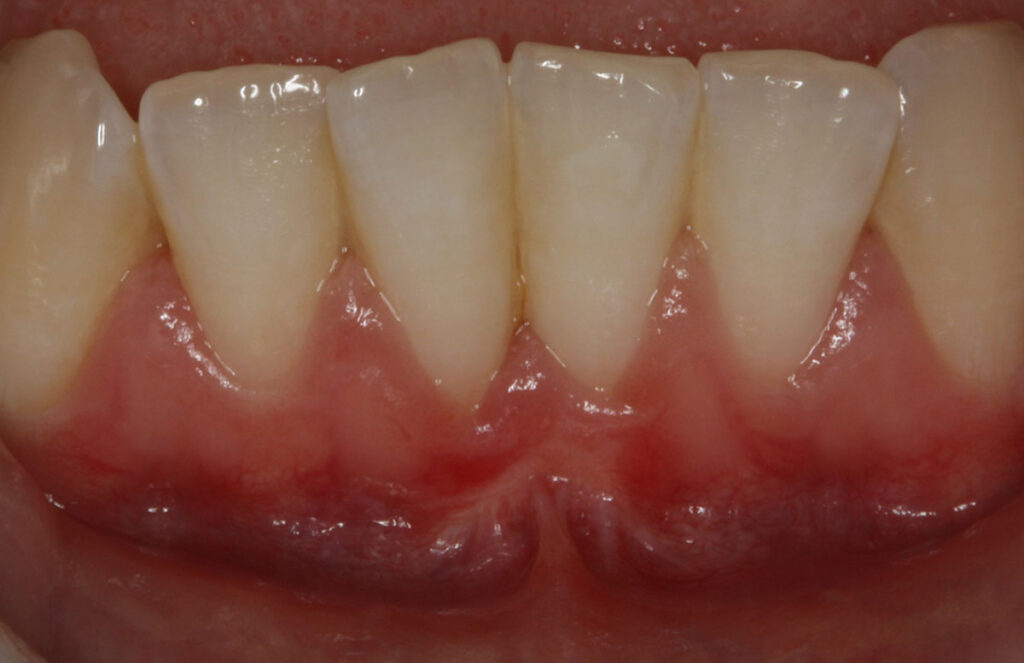
Other plastic periodontal surgical procedures are also performed, such as manipulating gingival tissue to cover root surfaces that have been exposed due to gingival recession.
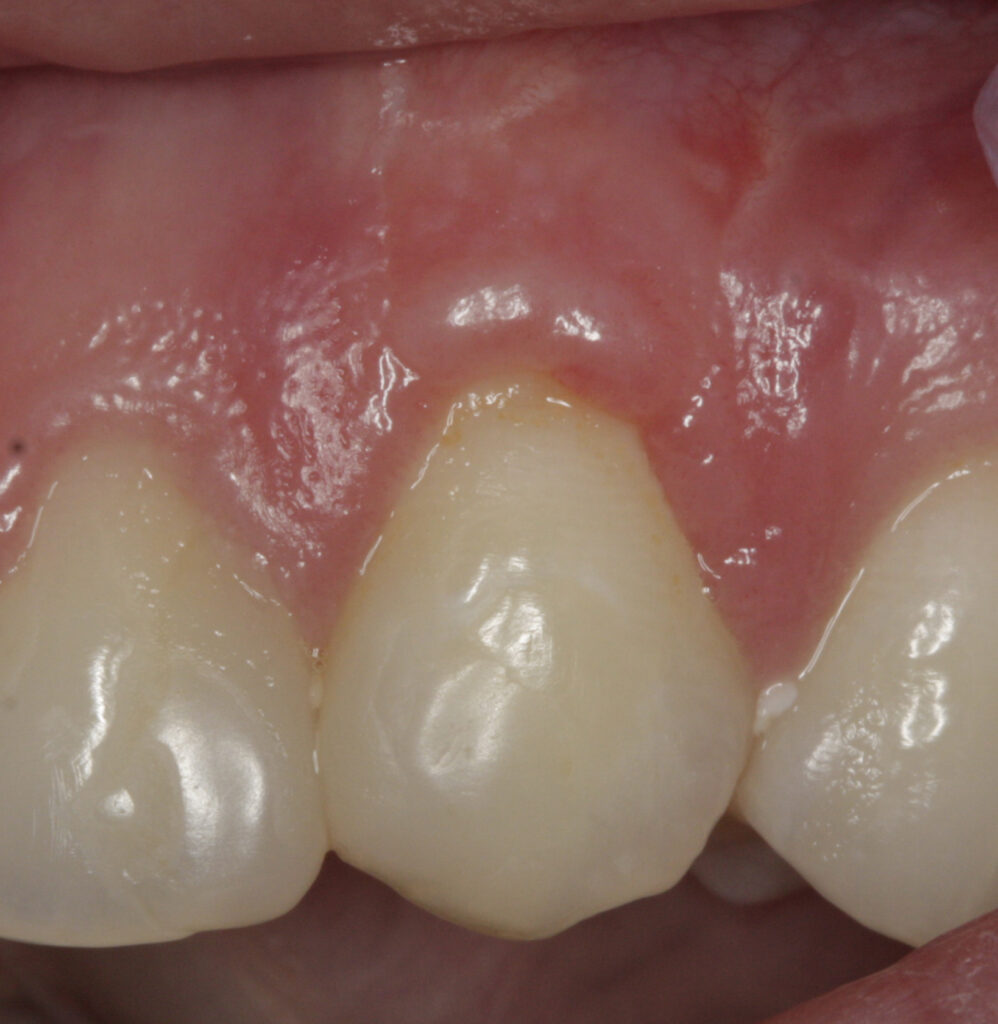
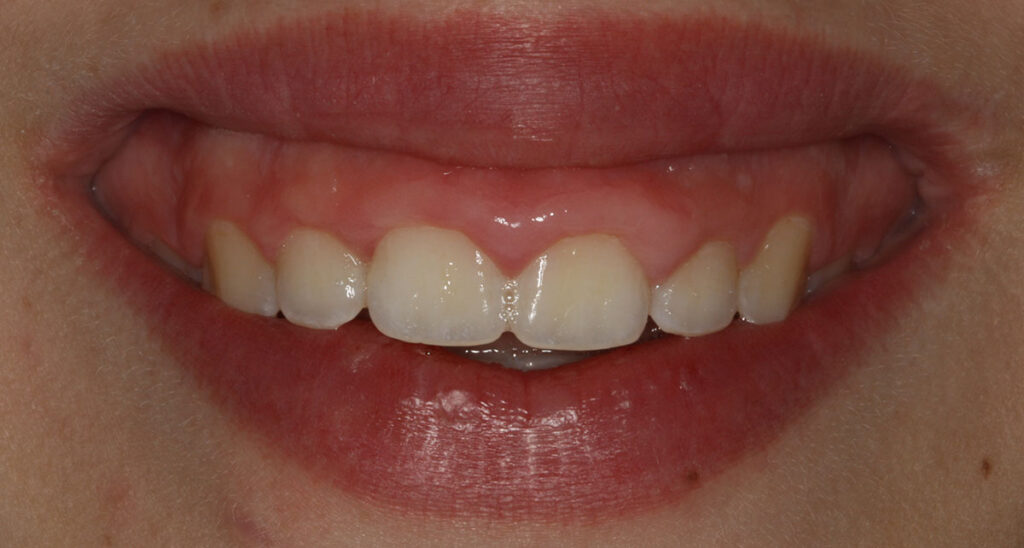
Soft tissue grafts are placed to reinforce and thicken weak, thin gums and may help to reduce the amount of gum shrinkage/recession on a root surface. This may improve the stability and appearance of the gums following the damage from periodontal disease, forceful toothbrushing, or tooth movement. The small area of gum tissue for the graft is usually taken from the roof of the mouth, which heals to its original appearance and contour over time.
Guided bone or tissue regeneration involves rebuilding the ridge of bone or supporting structures around a tooth. The changes can be the result of bone shrinkage after a tooth is removed or due to bone destruction due to the periodontitis. Different bone and molecular material can be used to restore the supporting structures, including your own bone, commercially produced bone particles, and enamel matrix derivative (EmdogainTM). The regeneration of bone and supporting structures can replace some or most of the tissues that have been lost in an area.
Crown lengthening makes a tooth appear longer, which may be needed to improve the aesthetics and symmetry of the gum margins, to make short teeth longer, or to increase the amount of tooth available to place a well-fitting filling or crown. This may involve removing some gum and bone around a tooth.
A frenectomy is a minor surgical procedure that involves removal of a small piece of soft tissue connecting the gums near the teeth to the mucosa on the inner lip. This may be needed if the gums are receding in the area due to the tension from the frenum, if the frenum interferes with brushing or with a denture, or if the frenum stops the space between two teeth being closed together during orthodontic treatment.
Periodontists also perform numerous other surgical procedures, including root resections, removal of excess overgrown gum, and orthodontic-related surgical procedures, such as frenectomies, exposures of impacted teeth, pericisions, and stimulation of the periodontium to increase speed of treatment.